Quickstart¶
Prefect is an orchestration and observability platform that empowers developers to build and scale code quickly, turning their Python scripts into resilient, recurring workflows.
In this quickstart, you'll see how you can schedule your code on remote infrastructure and observe the state of your workflows. With Prefect, you can go from a Python script to a production-ready workflow that runs remotely in a few minutes.
Let's get started!
Setup¶
Here's a basic script that fetches statistics about the main Prefect GitHub repository.
import httpx
def get_repo_info():
url = "https://api.github.com/repos/PrefectHQ/prefect"
response = httpx.get(url)
repo = response.json()
print("PrefectHQ/prefect repository statistics 🤓:")
print(f"Stars 🌠 : {repo['stargazers_count']}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
get_repo_info()
How can we make this script schedulable, observable, resilient, and capable of running anywhere?
Step 1: Install Prefect¶
pip install -U prefect
See the install guide for more detailed installation instructions, if needed.
Step 2: Connect to Prefect's API¶
Much of Prefect's functionality is backed by an API. The easiest way to get started is to use the API hosted by Prefect:
- Create a forever-free Prefect Cloud account or sign in at https://app.prefect.cloud/
- Use the
prefect cloud loginCLI command to log in to Prefect Cloud from your development environment
prefect cloud login
Choose Log in with a web browser and click the Authorize button in the browser window that opens.
Self-hosted Prefect server instance
If you would like to host a Prefect server instance on your own infrastructure, see the tutorial and select the "Self-hosted" tab. Note that you will need to both host your own server and run your flows on your own infrastructure.
Step 3: Turn your function into a Prefect flow¶
The fastest way to get started with Prefect is to add a @flow decorator to your Python function.
Flows are the core observable, deployable units in Prefect and are the primary entrypoint to orchestrated work.
import httpx # an HTTP client library and dependency of Prefect
from prefect import flow, task
@task(retries=2)
def get_repo_info(repo_owner: str, repo_name: str):
"""Get info about a repo - will retry twice after failing"""
url = f"https://api.github.com/repos/{repo_owner}/{repo_name}"
api_response = httpx.get(url)
api_response.raise_for_status()
repo_info = api_response.json()
return repo_info
@task
def get_contributors(repo_info: dict):
"""Get contributors for a repo"""
contributors_url = repo_info["contributors_url"]
response = httpx.get(contributors_url)
response.raise_for_status()
contributors = response.json()
return contributors
@flow(log_prints=True)
def repo_info(repo_owner: str = "PrefectHQ", repo_name: str = "prefect"):
"""
Given a GitHub repository, logs the number of stargazers
and contributors for that repo.
"""
repo_info = get_repo_info(repo_owner, repo_name)
print(f"Stars 🌠 : {repo_info['stargazers_count']}")
contributors = get_contributors(repo_info)
print(f"Number of contributors 👷: {len(contributors)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
repo_info()
Note that we added a log_prints=True argument to the @flow decorator so that print statements within the flow-decorated function will be logged.
Also note that our flow calls two tasks, which are defined by the @task decorator.
Tasks are the smallest unit of observed and orchestrated work in Prefect.
python my_gh_workflow.py
Now when we run this script, Prefect will automatically track the state of the flow run and log the output where we can see it in the UI and CLI.
14:28:31.099 | INFO | prefect.engine - Created flow run 'energetic-panther' for flow 'repo-info'
14:28:31.100 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - View at https://app.prefect.cloud/account/123/workspace/abc/flow-runs/flow-run/xyz
14:28:32.178 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Created task run 'get_repo_info-0' for task 'get_repo_info'
14:28:32.179 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Executing 'get_repo_info-0' immediately...
14:28:32.584 | INFO | Task run 'get_repo_info-0' - Finished in state Completed()
14:28:32.599 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Stars 🌠 : 13609
14:28:32.682 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Created task run 'get_contributors-0' for task 'get_contributors'
14:28:32.682 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Executing 'get_contributors-0' immediately...
14:28:33.118 | INFO | Task run 'get_contributors-0' - Finished in state Completed()
14:28:33.134 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Number of contributors 👷: 30
14:28:33.255 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Finished in state Completed('All states completed.')
You should see similar output in your terminal, with your own randomly generated flow run name and your own Prefect Cloud account URL.
Step 4: Choose a remote infrastructure location¶
Let's get this workflow running on infrastructure other than your local machine! We can tell Prefect where we want to run our workflow by creating a work pool.
We can have Prefect Cloud run our flow code for us with a Prefect Managed work pool.
Let's create a Prefect Managed work pool so that Prefect can run our flows for us. We can create a work pool in the UI or from the CLI. Let's use the CLI:
prefect work-pool create my-managed-pool --type prefect:managed
You should see a message in the CLI that your work pool was created. Feel free to check out your new work pool on the Work Pools page in the UI.
Step 5: Make your code schedulable¶
We have a flow function and we have a work pool where we can run our flow remotely. Let's package both of these things, along with the location for where to find our flow code, into a deployment so that we can schedule our workflow to run remotely.
Deployments elevate flows to remotely configurable entities that have their own API.
Let's make a script to build a deployment with the name my-first-deployment and set it to run on a schedule.
from prefect import flow
if __name__ == "__main__":
flow.from_source(
source="https://github.com/discdiver/demos.git",
entrypoint="my_gh_workflow.py:repo_info",
).deploy(
name="my-first-deployment",
work_pool_name="my-managed-pool",
cron="0 1 * * *",
)
Run the script to create the deployment on the Prefect Cloud server.
Note that the cron argument will schedule the deployment to run at 1am every day.
python create_deployment.py
You should see a message that your deployment was created, similar to the one below.
Successfully created/updated all deployments!
Deployments
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Name ┃ Status ┃ Details ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━┩
│ repo-info/my-first-deployment │ applied │ │
└───────────────────────────────┴─────────┴─────────┘
To schedule a run for this deployment, use the following command:
$ prefect deployment run 'repo-info/my-first-deployment'
You can also run your flow via the Prefect UI: <https://app.prefect.cloud/account/abc/workspace/123/deployments/deployment/xyz>
Head to the Deployments page of the UI to check it out.
Code storage options
You can store your flow code in nearly any location. You just need to tell Prefect where to find it. In this example, we use a GitHub repository, but you could bake your code into a Docker image or store it in cloud provider storage. Read more here.
Push your code to GitHub
In the example above, we use an existing GitHub repository.
If you make changes to the flow code, you will need to push those changes to your own GitHub account and update the source argument to point to your repository.
You can trigger a manual run of this deployment by either clicking the Run button in the top right of the deployment page in the UI, or by running the following CLI command in your terminal:
prefect deployment run 'repo-info/my-first-deployment'
The deployment is configured to run on a Prefect Managed work pool, so Prefect will automatically spin up the infrastructure to run this flow. It may take a minute to set up the Docker image in which the flow will run.
After a minute or so, you should see the flow run graph and logs on the Flow Run page in the UI.
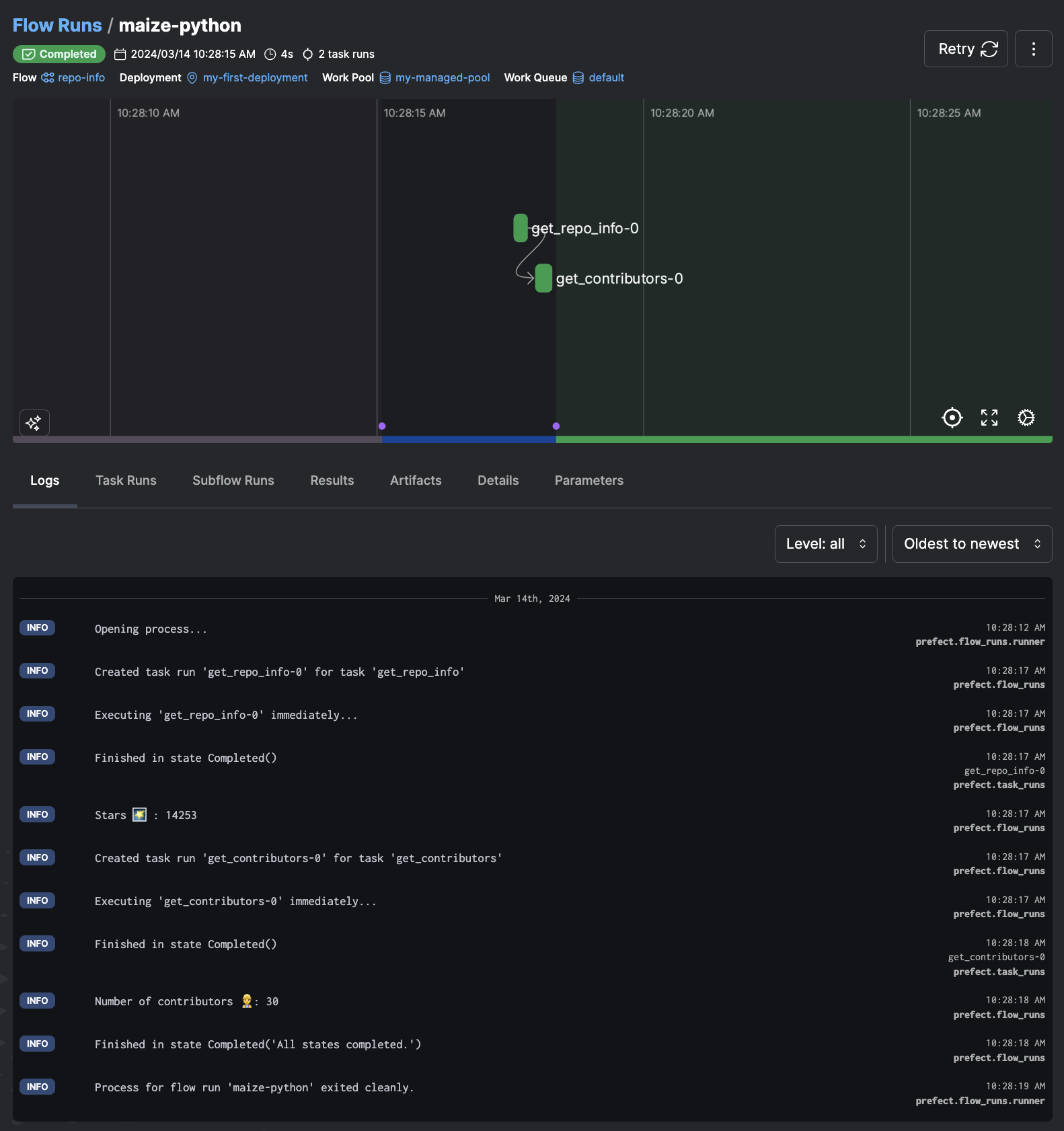
Remove the schedule
Click the Remove button in the top right of the Deployment page so that the workflow is no longer scheduled to run once per day.
Next steps¶
You've seen how to move from a Python script to a scheduled, observable, remotely orchestrated workflow with Prefect.
To learn how to run flows on your own infrastructure, see how to customize the Docker image where your flow runs, and see how to gain lots of orchestration and observation benefits check out the tutorial.
Need help?
Get your questions answered by a Prefect Product Advocate! Book a Meeting
Happy building!